Psychological symptoms of multiple sclerosis
When it comes to multiple sclerosis, attention is usually focused on the physical symptoms that patients may have. However, it is also important to be aware of the psychological symptoms that those with the disease can experience.
Many patients with multiple sclerosis are affected by feelings of anxiety and depression. Patients can constantly feel anxious about their future and the progression of the disease. Some may also experience low mood and severe depression, affecting their overall quality of life.
Some patients may have difficulty dealing with the physical changes they undergo due to the disease, which affects their self-esteem and self-image. They feel dissatisfied with themselves and may suffer from personality disorder.
As time passes and the disease progresses, psychological symptoms can increase and include social isolation and loss of interest in activities that once brought the person with the disease happiness.
It is important for people with multiple sclerosis to be supported psychologically and to obtain the necessary psychological support from family, friends, and medical teams. Paying attention to the psychological aspect of the disease can help improve their quality of life and enhance their overall health.

What are the symptoms of a multiple sclerosis attack?
A multiple sclerosis attack is an event that occurs when the disease develops suddenly and increases in severity over a short period of time. Attacks can have different symptoms and vary between people. However, there are some common symptoms that can appear during a psychological attack of MS.
One of the main symptoms is poor coordination and movement. Control of movement may become more difficult and walking may become uneven. Patients may have difficulty with balance and visual impairment.
Moreover, a psychogenic MS attack can be accompanied by other disturbing symptoms such as fatigue, general weakness, dizziness and vertigo, nervous itching and tingling.
Knowing these symptoms is important for patients, their family members, and health providers to identify and treat attacks effectively. You should immediately consult a doctor if you think you are suffering from an attack of multiple sclerosis.
How does multiple sclerosis begin?
When it comes to the symptoms of multiple sclerosis, early detection is very important. However, it may be difficult to recognize the onset of multiple sclerosis in the first stage, as symptoms can be very mild or similar to those of other diseases.
One of the first signs of multiple sclerosis is a feeling of inexplicable fatigue and exhaustion. You may feel excessively tired even after adequate rest and sleep. It may be difficult for some people to pinpoint the cause of this persistent fatigue.
Some people can also feel numbness or weakness in some parts of the body, such as the feet or hands. This may be a result of damage to the nerve level in the brain and nervous system, which occurs in neurosclerosis.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor to evaluate your condition. Early diagnosis can help initiate appropriate treatment and psychological management of multiple sclerosis.
Is multiple sclerosis related to psychology?
It is known that multiple sclerosis is a chronic condition that affects the central nervous system. However, there is evidence to suggest that multiple sclerosis also affects the psychological state of people with it.
For many patients with multiple sclerosis, changes in mood and emotion may occur. People with this type of injury can feel depressed, anxious, and depressed. The daily challenges that patients face, such as difficulties with movement and the ability to perform daily activities, can cause psychological and emotional stress.
It is important to pay attention to the psychological aspect of people with multiple sclerosis and provide them with the necessary support. Healthy strategies such as practicing meditation, participating in recreational activities, and connecting with social support can help improve the psychological well-being of people with this disease.
Don't forget that if you feel depressed or severely anxious, you should contact your healthcare provider to get appropriate help.
Does multiple sclerosis cause anxiety?
The answer may vary from person to person, but for many people with multiple sclerosis, they suffer from feelings of anxiety and stress due to the daily challenges they face. Multiple sclerosis may affect a person's ability to move and perform daily tasks, which can cause a feeling of helplessness and anxiety.
In addition, multiple sclerosis may affect the emotional and moral aspects of a person, as they can feel depressed or sad, which can also lead to anxiety.
If you have multiple sclerosis and are concerned, it is important that you speak to your doctor for appropriate support and advice. Your doctor may recommend anxiety management techniques or enlist the help of psychological experts to help deal with anxiety related to multiple sclerosis.
How long does it take between attacks of multiple sclerosis?
Multiple sclerosis attacks are the result of damage to the immune system and its attack on the central nervous system, and symptoms and attacks are classified based on their nature and severity. The length of time between attacks may vary from person to person, and you may have frequent attacks or long drainage periods between attacks.
Usually, a multiple sclerosis attack occurs suddenly and lasts for a short period, which may be a few hours or several days, and then gradually fades away. The person may feel a gradual improvement in symptoms during this period, but symptoms may be affected differently in each attack.
Whatever the length of time between attacks, self-care and appropriate medical support can help manage symptoms and reduce their impact on daily life. Consult a specialist doctor to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for your individual condition.
How do you know you have multiple sclerosis?
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that affects the body's immune system. Multiple sclerosis is a common neurological disease that affects the central nervous system. People with MS experience many different symptoms, including difficulty walking, irregular jerking movements, muscle weakness, and pain in the nerves, muscles and joints. Symptoms of multiple sclerosis appear separately in affected individuals, as the patient may suffer from depression, muscle weakness, muscle stiffness, tingling, numbness or pain in different parts of the body. You should see a doctor to diagnose multiple sclerosis and get appropriate treatment.
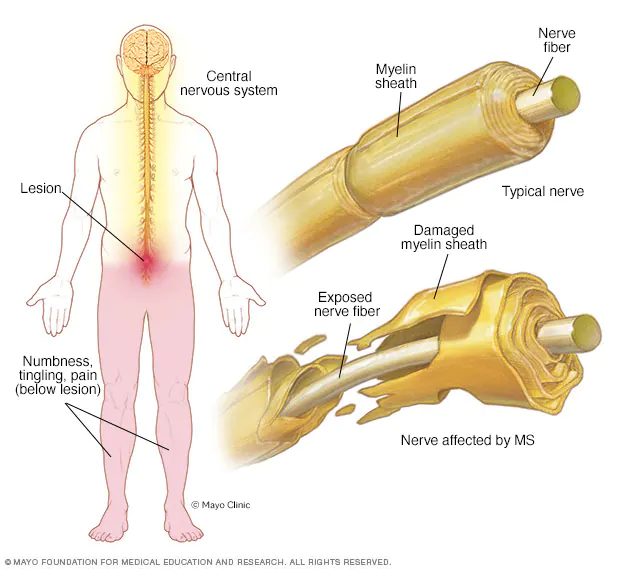
What diseases resemble multiple sclerosis?
There are many diseases that are similar to multiple sclerosis in terms of symptoms and impact on mental health. Among these diseases:
- Chronic fatigue: Chronic fatigue is characterized by frequent feelings of extreme fatigue and exhaustion, and can negatively affect your mood and ability to concentrate.
- Depression: Depression causes feelings of constant sadness and loss of interest in things that were enjoyable in the past, and can lead to a low level of energy and self-care.
- Anxiety: Multiple sclerosis can be accompanied by constant anxiety and excessive anxiety, which can affect the ability to relax and deal with daily challenges.
- Sleep disorders: Sleep disorders can be common in people with multiple sclerosis, and include insomnia and frequent waking during the night.
- Low mood: Multiple sclerosis can lead to low mood, feelings of depression, and general tension.
It is worth noting that these diseases are not necessarily multiple sclerosis, but are sometimes similar to its symptoms and impact on mental health. It is important to consult a doctor to accurately diagnose the condition and get appropriate treatment.
When is multiple sclerosis detected?
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, affecting the nerves and spinal cord. Although there is no specific time to detect it, there are some signs that can indicate the presence of the disease.
It is difficult to determine the exact onset of the disease, as symptoms can develop gradually over time. You may notice some initial symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, and numbness in the extremities. These symptoms may be mild at first, but they worsen over time.
The disease is usually detected after symptoms of fatigue or weakness appear in the nervous system. You may need tests and scans to confirm the diagnosis, including an MRI and cerebrospinal fluid examination.
It is important to stay in touch with your doctor and report any changes in overall health. If you feel any abnormal symptoms or suspect a health problem, be sure to see your doctor to evaluate the condition and get appropriate treatment.
Does multiple sclerosis cause back pain?
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system and can cause a variety of symptoms. Among these possible symptoms, back pain may be one of them.
In some cases, patients with multiple sclerosis experience back pain due to the disease's effect on the central nervous system. Multiple sclerosis can affect the nerves that control body functions, including the back and accessory organs.
However, it should be noted that back pain may also be a result of other factors, such as psychological stress or tight muscles. Therefore, patients with multiple sclerosis are advised to consult with specialist doctors to determine the cause of the pain and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
It is good to mention that there are treatment options available to deal with back pain associated with multiple sclerosis, such as physical therapy, appropriate physical exercises, and learning mental training techniques. It is recommended to exercise regularly and maintain a healthy lifestyle to support the back and reduce symptoms associated with multiple sclerosis.
Does multiple sclerosis affect speech?
When it comes to multiple sclerosis, it can affect many different aspects of daily life. One of these aspects is speech. Many people with multiple sclerosis have difficulties with speech and verbal communication.
Multiple sclerosis can lead to abnormalities in the muscles responsible for tongue and mouth movement, making speech slurred and difficult to understand. You may feel upset and embarrassed when you are unable to express what you are thinking clearly.
However, some measures can be taken to deal with these difficulties. Speech and breathing enhancement techniques can be helpful to mitigate negative effects on speech. Muscle-strengthening exercises may also help improve movement and control of the tongue and mouth.
Although multiple sclerosis may affect speech, it does not mean there has to be frustration. People with multiple sclerosis can learn and use alternative communication methods such as speech aids and writing apps to keep communication smooth.
So, if you suffer from multiple sclerosis and find it difficult to speak, there is no need to despair. There are different methodologies you can explore to deal with these difficulties and maintain effective communication.
Has anyone recovered from multiple sclerosis?
Unfortunately, there is still no complete cure for multiple sclerosis. This chronic disease affects the central nervous system and usually develops slowly over time. However, patients can live good, productive lives with multiple sclerosis by managing symptoms and maintaining good health.
There are several ways to deal with multiple sclerosis psychologically. Seeking psychosocial support from friends and family can be helpful in dealing with daily challenges and coping with changes in life. Consultation with a qualified psychologist may also be necessary, as they can provide support and guidance to patients and their family members.
As difficult as multiple sclerosis is, there is still hope. Research and treatments are constantly being developed, and may one day bring a comprehensive treatment or even a cure. For now, patients should focus on managing symptoms and living on a positive note to have the best quality of life possible.
Does sadness affect patients with multiple sclerosis?
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system, and studies have shown that psychological factors can play an important role in the development and worsening of this disease.
When patients are exposed to constant sadness, this can negatively affect their psychological and mental state. In addition, sadness may increase stress and anxiety, which ultimately worsens the symptoms of multiple sclerosis.
At the same time, feeling happy and satisfied can contribute to improving the condition of patients with multiple sclerosis. Feeling positive and optimistic helps reduce stress, enhance mental health, and improve quality of life.
Therefore, it is important for patients with multiple sclerosis to try to deal positively with negative emotions and sadness, and to strive to relax and appreciate the positive aspects of their lives. It may also be helpful for them to look into stress management strategies, such as meditation or light exercise.
Is neuritis multiple sclerosis?
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. Although the causes of the disease are still not fully known, neuritis is not necessarily multiple sclerosis.
However, there is some research suggesting that nerve infections can cause symptoms similar to multiple sclerosis, such as muscle weakness, numbness and partial paralysis. If you feel any of these symptoms, it is important that you consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Although it can be difficult to differentiate between multiple sclerosis and neuritis based on symptoms alone, medical tests such as MRIs and blood tests can help determine the correct diagnosis.
It is important to know that the appropriate treatment varies greatly between multiple sclerosis and neuritis, so it is necessary to consult a specialist doctor to obtain an accurate diagnosis and the necessary treatment.
Does multiple sclerosis appear on an MRI?
When an MRI scan is performed to diagnose multiple sclerosis, some subtle signs and changes may appear in the images that are taken. However, an MRI scan alone cannot definitively identify multiple sclerosis, and requires confirmation of the diagnosis and understanding of its other symptoms through medical consultation.
The MRI shows some changes associated with multiple sclerosis, such as the presence of sclerosis in the brain and various nerve cords. Fibrosis and enlargement of nerve tissue, and changes in the size of some areas of the brain, may also appear. However, these changes are non-specific and not exclusive to multiple sclerosis, and can also occur in other neurological conditions.
Overall, an MRI scan can be useful as an additional diagnostic tool for multiple sclerosis, but it is not the only factor used to determine the final diagnosis. Identifying psychogenic MS requires a comprehensive analysis of symptoms and other tests, and consultation with doctors who specialize in neurological diseases.